Automate your git cleanup! Here's a shell function to add to your bashrc/zshrc file to delete all merged git branches in one command.
⚠️ This post is over two years old and may contain some outdated technical information. Please proceed with caution!
Are you feeling overwhelmed with too many git branches? Do you know which branches have been merged and which can be safely deleted? Do you leave your git branches to pile up on your local machine until your git branch command spits out one hundred terminal pages of text? There's no need to live like this!
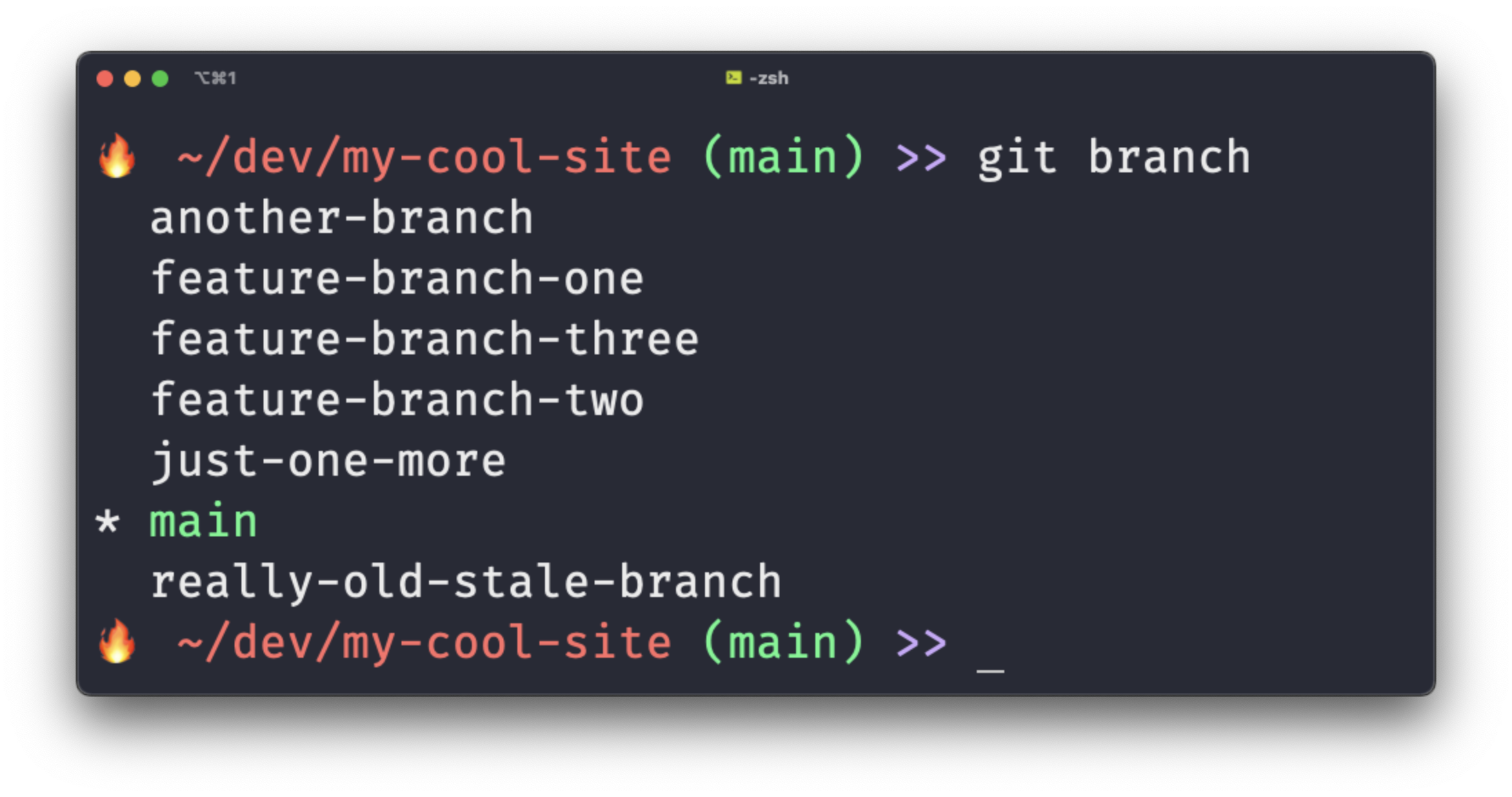
Here's how you can safely delete all merged git branches with one terminal command, using a little shell function.
The script
To delete all merged git branches on your local machine:
add the following code to your
.bashrcor.zshrcfile (switch outmainfor what you usually call your main branches if necessary)save the file
source the new changes (or reload your terminal)
run
damin a git project directory (dam is my acronym for delete all merged)and it's done!
# delete all branches merged into main
dam() {
echo "=== Deleting all merged branches ==="
git checkout main && git branch --merged | egrep -v "(^\*|main)" | xargs git branch -d
echo "☑️ Done!"
}In short, the code above checks out the main branch, lists all merged branches, searches for and lists branches that are not named exactly "main", and uses git to delete those branches on your local machine.
Here's a detailed breakdown.
git checkout main && git branch --merged
This command checks out the main branch, and lists all branches that can be detected as being merged into the main branch. The official git documentation writes this as "list branches whose tips are reachable from the specified commit (HEAD if not specified)". We're not specifying a commit, so the command will use the HEAD — the current local state of the main branch.
| egrep -v "(^\*|main)"
We use egrep (or extended grep) to search using extended regular expressions. The -v flag instructs egrep to print lines that do not match a given regular expression. The regular expression we're passing in — "(^\*|main)" — matches the characters "main" from the start of the line. So with the -v flag, we're asking egrep to find every branch that isn't named "main".
The | (or pipe) at the beginning of the line means we're "piping" — or sending — the output of the previous command (git branch --merged) into egrep to perform the regular expression search. Read more about egrep.
| xargs git branch -d
Finally, we pipe the result of the egrep search to the xargs command (short for extended arguments). xargs takes input from standard input (basically, a string of text — or a list of git branches in this case), and splits the string where there are spaces into separate arguments that can be used in a command.
For each of the branches returned by egrep above, the script will run git branch -d, which will delete the branch on your local machine.
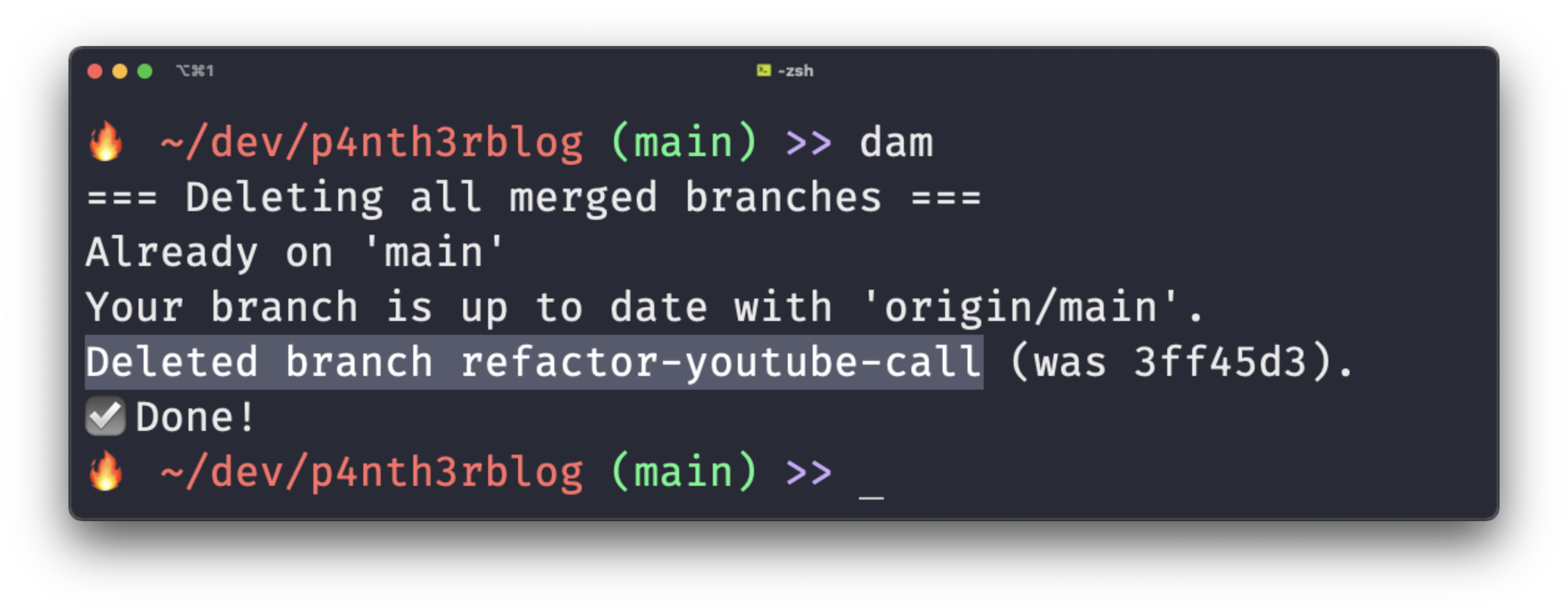
And here's the script in action in the terminal. Enjoy!

Salma Alam-Naylor
I'm a live streamer, software engineer, and developer educator. I help developers build cool stuff with blog posts, videos, live coding and open source projects.